Exploring Google Analytics Secondary Dimension: Methods and Benefits
Opening the Power of Secondary Measurement Analytics for Enhanced Data Insights and Decision-Making
In the realm of information analytics, primary dimensions commonly take the limelight, but real deepness of understandings exists within the realm of secondary measurements. These added data points provide a nuanced viewpoint that can brighten patterns and relationships not easily evident at initial glance. By utilizing the power of additional dimension analytics, companies can reveal concealed fads, reveal correlations, and extract a lot more significant conclusions from their information. The potential for enhanced decision-making through the utilization of these secondary dimensions is vast, promising a deeper understanding of complex data collections and leading the way for even more enlightened critical selections.
Importance of Second Measurements
Checking out the significance of second measurements in analytics reveals the hidden layers of information insights essential for informed decision-making in numerous domains. Secondary measurements offer a deeper understanding of key data by offering added context and point of views. By incorporating second dimensions into analytics, companies can draw out a lot more comprehensive and nuanced understandings from their datasets.
One key relevance of additional dimensions is their ability to segment and categorize primary information, enabling an extra in-depth analysis of certain subsets within a dataset. This division makes it possible for services to identify patterns, patterns, and outliers that might not appear when taking a look at the information overall. Second dimensions help in discovering relationships and dependencies between different variables, leading to even more exact projecting and predictive modeling - secondary dimension.
Additionally, additional measurements play a crucial function in improving information visualization and coverage. By including second measurements to visualizations, such as charts or graphs, analysts can produce a lot more informative and informative representations of data, helping with far better communication of findings to stakeholders. In general, the combination of additional dimensions in analytics is critical in opening the complete capacity of data and driving evidence-based decision-making.
Secret Advantages of Making Use Of Second Dimensions
Making use of additional dimensions in analytics uses organizations a critical advantage by augmenting the deepness and granularity of data understandings. By dissecting information using second dimensions such as time, area, gadget kind, or individual demographics, companies can discover patterns, fads, and connections that might otherwise continue to be hidden.
In addition, the utilization of secondary dimensions improves the context in which main information is analyzed. By leveraging secondary dimensions in analytics, organizations can harness the full capacity of their data to drive much better decision-making and accomplish their organization purposes.
Advanced Information Evaluation Techniques
A deep study advanced data analysis techniques reveals advanced approaches for removing beneficial understandings from intricate datasets. One such strategy is artificial intelligence, where formulas are used to recognize patterns within information, anticipate results, and make data-driven decisions. This method permits the automation of analytical version structure, making it possible for the handling of big volumes of data at a faster rate than typical approaches.
One more sophisticated technique is predictive analytics, which makes use of analytical algorithms and device learning techniques to forecast future results based on historical information. By examining patterns and patterns, businesses can prepare for client behavior, market trends, and possible dangers, equipping them to make proactive choices.
Moreover, text mining and sentiment evaluation are useful techniques for removing understandings from unstructured information resources such as social networks comments, consumer evaluations, and survey reactions. By analyzing message information, organizations can recognize client opinions, recognize emerging fads, and improve their service or products based on comments.
Enhancing Decision-Making Through Additional Dimensions
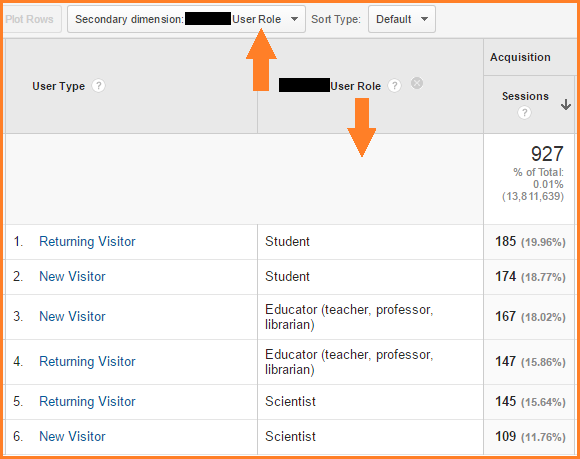
Enhancing decision-making via second dimensions allows organizations to make even more informed and targeted calculated choices. For example, by segmenting client information based on secondary dimensions like buying background or engagement levels, business can customize their advertising and marketing strategies to particular target market sectors, leading to improved conversion rates and client fulfillment. Additional dimensions can help identify correlations and relationships in between various variables, allowing organizations to make data-driven decisions that drive development and productivity.
Applying Second Dimension Analytics
When integrating secondary measurements in analytics, companies can unlock deeper understandings that drive critical decision-making and improve general performance. Applying second dimension analytics requires an organized technique to guarantee effective application of this effective tool. The initial action is to identify the vital metrics and measurements that align with the company's calculated goals. This requires comprehending the particular inquiries the company seeks to address and the data factors needed to resolve them.
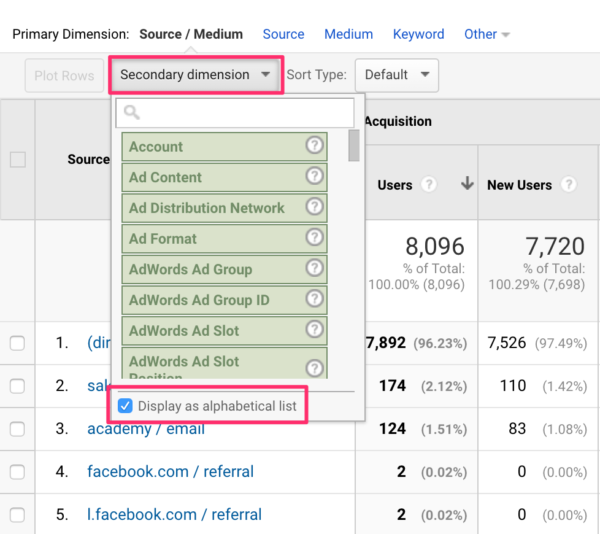
Additionally, companies should take advantage of progressed analytics tools and innovations to simplify the process of integrating second dimensions. These tools can automate information handling, analysis, and visualization, enabling companies to concentrate on interpreting insights as opposed to hand-operated data manipulation.
Final Thought
Finally, secondary dimension analytics play a vital duty in enhancing data insights and decision-making processes. By using innovative information analysis techniques and executing additional measurements properly, organizations can unlock the power of their our website data to drive tactical service choices. The crucial advantages of making use of second measurements can not be overemphasized, as they give a much deeper understanding of data trends and relationships. It is important for organizations to take advantage of additional dimension analytics to stay competitive in today's data-driven landscape.
In the world of data analytics, primary dimensions frequently take the limelight, however the true deepness of understandings exists within the world of additional dimensions.Making use of additional dimensions in analytics offers companies a strategic benefit by increasing the depth and granularity of information understandings. By leveraging secondary measurements in analytics, link companies can harness the full possibility of their information to drive better decision-making and attain their service objectives.
Implementing information validation procedures and routine audits can help preserve data top quality and dependability.
By utilizing innovative data evaluation techniques and applying additional measurements efficiently, companies can unlock the power of their information to drive calculated company choices.